The Global Renewable Energy Transition in 2026: Markets, Power, and the New Energy Economy
The global energy system in 2026 is undergoing one of the most profound structural shifts in modern economic history, and for the audience of upbizinfo.com, this shift is no longer an abstract environmental debate but a central driver of strategy across finance, technology, employment, and markets. The long-standing reliance on fossil fuels is steadily yielding to a renewable-centric model, reshaping how capital is allocated, how companies compete, how governments pursue security, and how societies define long-term prosperity. What began as a climate imperative has evolved into a decisive economic, technological, and geopolitical transformation that touches every business domain covered by upbizinfo.com, from AI and technology to banking and investment, employment, and global markets.
From Climate Imperative to Strategic Economic Shift
The urgency of the transition is driven by converging forces: intensifying climate risks, volatility in oil and gas prices, rapid cost declines in renewables, and rising expectations from regulators, investors, and consumers. The International Energy Agency (IEA) now projects that renewables will account for well over half of global power generation before 2035, with solar and wind continuing to dominate new capacity additions. This structural pivot is altering fiscal policy in hydrocarbon-dependent economies, redirecting capital flows in global markets, and forcing a reconfiguration of supply chains on every continent.
For the business community, especially in major economies such as the United States, European Union, China, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, Japan, and South Korea, energy strategy has become inseparable from competitiveness and risk management. Firms that once treated energy procurement as a back-office function now view it as a core lever of cost control, resilience, and brand trust. Readers of upbizinfo.com see this shift play out daily in corporate news and policy developments, where energy decisions are tightly linked to valuations, regulatory exposure, and long-term growth narratives.
Policy, Regulation, and International Cooperation
Policy remains the most powerful accelerator of the renewable transition, and by 2026, governments have moved from broad pledges to more granular, enforceable frameworks. The Paris Agreement continues to provide the overarching structure for global climate ambition, but its credibility now rests on national implementation plans, carbon pricing regimes, and sector-specific regulations that materially influence corporate decisions.
In Europe, the European Green Deal and the Fit for 55 package have entrenched the European Union as a regulatory pacesetter. Through mechanisms such as the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and reforms to the EU Emissions Trading System, the bloc has effectively tied access to its vast market to decarbonization performance, influencing producers from Germany to China and from Spain to Brazil. The European Investment Bank (EIB), which has reoriented its mandate toward climate action, has become a central pillar in financing clean infrastructure and innovation across the continent and beyond. Learn more about how these shifts are influencing global economic governance and trade by exploring upbizinfo.com/economy.html.
In the United States, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) has matured into one of the most consequential industrial policies of the century. Its long-term tax credits for clean power, storage, hydrogen, and electric vehicles have catalyzed a wave of manufacturing investment across states such as Texas, Georgia, and Ohio, while reinforcing the clean-tech ecosystems in California and New York. This policy-driven reshoring of energy and battery supply chains is reshaping North American competitiveness and has triggered strategic responses in Canada, Mexico, and key partners in Europe and Asia. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), through its Loan Programs Office and innovation hubs, has further strengthened the commercialization pipeline for advanced technologies including long-duration storage, small modular reactors, and green hydrogen.
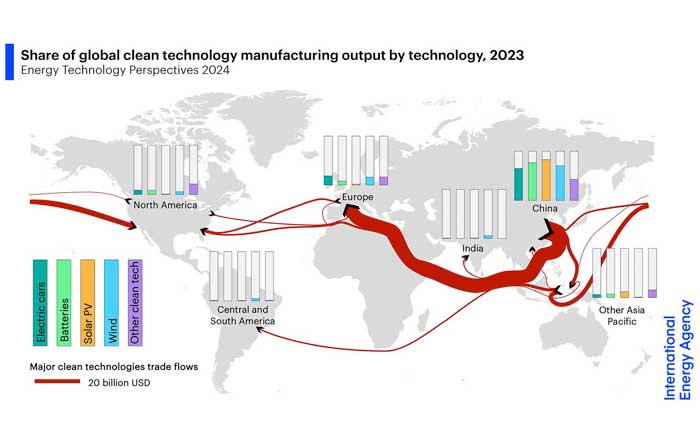
In Asia, national strategies such as China's 2060 carbon neutrality goal, Japan's Green Transformation (GX) program, and South Korea's Green New Deal are accelerating deployment while nurturing domestic champions in solar, wind, batteries, and electric vehicles. China remains the anchor of global clean-tech manufacturing, but it is also tightening environmental standards and investing heavily in ultra-high-voltage transmission and digital grid infrastructure. Meanwhile, initiatives such as the International Solar Alliance highlight how emerging powers like India are shaping the diplomatic architecture of the energy transition.
Multilateral institutions including the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) are embedding climate considerations into lending, surveillance, and development programs, further aligning global capital with decarbonization goals. For executives and investors following upbizinfo.com/world.html, these policy and diplomatic trends are essential context for understanding country risk, market access, and regulatory trajectories.
Technology, AI, and the New Energy Stack
The technical foundations of the renewable transition have advanced at a pace that would have seemed improbable a decade ago. Solar photovoltaics, onshore and offshore wind, grid-scale batteries, and digital control systems now form a highly competitive "new energy stack" that is increasingly able to meet baseload, peak, and flexibility needs once served exclusively by fossil fuels.
Solar module efficiencies continue to rise, driven by innovations in perovskite tandem cells and advanced manufacturing techniques pioneered by companies in China, United States, Germany, and Japan. Offshore wind is entering deeper waters through floating platforms developed by firms such as Equinor and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, unlocking vast resources off the coasts of United Kingdom, Norway, France, Spain, South Korea, and Japan. At the same time, battery manufacturers like CATL, LG Energy Solution, and Panasonic are scaling new chemistries, including sodium-ion and solid-state designs, to reduce costs and mitigate raw material constraints.
Artificial intelligence has become a critical layer in this system. AI-driven forecasting, grid optimization, and predictive maintenance allow grid operators and asset owners to manage high shares of variable renewables without sacrificing reliability. Research teams at Google DeepMind, IBM, and leading utilities are deploying machine learning models that integrate high-resolution weather data, consumption patterns, and market signals to optimize dispatch and storage in real time. This is where the intersection between energy and digital transformation-central to the editorial focus of upbizinfo.com/technology.html and upbizinfo.com/ai.html-is most visible, as energy becomes a data-intensive, software-defined service.
Hydrogen, particularly green hydrogen produced from renewable electricity, is emerging as a strategic technology for decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors such as steel, cement, chemicals, shipping, and aviation. Large-scale projects like the NEOM Green Hydrogen Company in Saudi Arabia and European initiatives coordinated through Hydrogen Europe illustrate how new industrial ecosystems are forming around hydrogen production, transport, and end-use. These developments are being closely monitored by investors and policymakers who read upbizinfo.com/investment.html to understand where the next wave of value creation may occur.
Capital, Banking, and the Financing Architecture of Transition
The energy transition is, at its core, a capital reallocation story. Trillions of dollars are being shifted from fossil-intensive assets toward renewables, grids, storage, and efficiency. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) and analyses by organizations such as BloombergNEF, annual clean energy investment has already surpassed annual fossil fuel investment, and by 2030, cumulative investments in the transition are expected to run into the tens of trillions of dollars.
Global banks, asset managers, and insurers have embedded climate risk and opportunity into their core business models. Institutions such as BlackRock, Goldman Sachs, HSBC, and JPMorgan Chase have developed dedicated sustainable finance platforms, underwriting green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, and transition finance products that support decarbonization in sectors where immediate full electrification is not yet feasible. The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and its successor frameworks have pushed climate risk reporting into the mainstream, making emissions profiles and transition plans integral to credit assessment and equity valuation. For readers of upbizinfo.com/banking.html, these shifts are redefining what it means to be a competitive financial institution in the 2020s.
On the sovereign and multilateral side, the Green Climate Fund (GCF), World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB), and regional development banks such as the African Development Bank (AfDB) are scaling blended finance structures that de-risk private investment in emerging markets across Africa, Asia, and South America. Green bond markets, tracked by organizations like the Climate Bonds Initiative, have grown into a multi-trillion-dollar asset class, providing a transparent and standardized channel for funding renewable projects, resilient infrastructure, and low-carbon transport.
For investors and corporate strategists who rely on upbizinfo.com to interpret these developments, the key implication is clear: capital is increasingly discriminating in favor of credible, forward-looking transition strategies, and firms that fail to adapt face rising financing costs, stranded asset risks, and reputational damage.
Employment, Skills, and the New Energy Workforce
The global labor market is being reshaped by the renewable transition in ways that directly affect business planning, workforce development, and social stability. According to IRENA and the International Labour Organization (ILO), renewable energy and related sectors employed well over 13 million people by the mid-2020s, with strong growth in solar, wind, batteries, and energy efficiency services. This has created new career paths in engineering, project finance, digital operations, and maintenance, spanning regions from United States and Germany to India, China, Brazil, South Africa, and Saudi Arabia.
At the same time, coal, oil, and gas sectors are contracting or restructuring, particularly in regions such as the Appalachian states in the U.S., coal regions of Poland and Germany, and mining communities in Australia and South Africa. Governments and companies are under pressure to design just transition strategies that provide retraining, mobility, and social protection to affected workers. Programs like South Africa's Just Energy Transition Partnership, supported by partners including the European Union, United Kingdom, and United States, serve as early models of how climate finance can be coupled with labor and regional development policy.
Education systems and corporate training programs are responding with new curricula in renewable engineering, data-driven energy management, and sustainability leadership. Universities and technical institutes across United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and Nordic countries are launching specialized degrees and micro-credentials tailored to the needs of clean energy employers. For professionals following upbizinfo.com/employment.html and upbizinfo.com/jobs.html, the message is that energy literacy, digital skills, and climate fluency are fast becoming baseline requirements across a wide range of roles, not just in traditional engineering functions.
Geopolitics, Critical Minerals, and Energy Security
As renewables expand, the geopolitics of energy is shifting from oil and gas chokepoints to technology leadership and mineral supply chains. Traditional energy exporters in the Middle East, Russia, and parts of Africa and South America are grappling with the prospect of long-term demand erosion for hydrocarbons, prompting diversification strategies that include large-scale investments in solar, wind, hydrogen, and clean-tech manufacturing. Initiatives such as Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 and United Arab Emirates' clean energy programs reflect attempts to reposition these economies as energy transition leaders rather than laggards.
At the same time, new forms of dependency are emerging around critical minerals such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and rare earth elements, heavily concentrated in countries like Chile, Democratic Republic of Congo, China, and Australia. The Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) and similar initiatives aim to build more resilient, transparent, and sustainable supply chains that reduce the risk of single-country dominance and address environmental and human rights concerns associated with mining. Resources from organizations like the International Energy Agency and the World Economic Forum are increasingly used by policymakers and executives to map these risks and opportunities.
For readers of upbizinfo.com/world.html, this evolving landscape underscores a critical insight: energy security in the renewable era is less about controlling a few strategic fuels and more about ensuring diversified access to technologies, materials, and intellectual property, supported by robust alliances and international norms.
Decentralization, Digitalization, and New Market Models
One of the most transformative features of the renewable era is the decentralization of power generation. Rooftop solar, community wind projects, and microgrids in regions from California to Germany, India, Kenya, and Thailand are enabling households, businesses, and local governments to become "prosumers" that both consume and produce electricity. This trend is particularly significant in emerging markets across Africa, South Asia, and Southeast Asia, where decentralized solutions are often the fastest and most cost-effective path to universal access.
Digitalization underpins this decentralization. Smart meters, IoT devices, and cloud-based platforms allow granular monitoring and control of distributed assets, while blockchain-based systems are being tested to enable peer-to-peer energy trading and transparent tracking of renewable certificates. Companies such as Energy Web, Powerledger, and utility innovators in Netherlands, Singapore, and Japan are demonstrating how these architectures can enhance efficiency, empower consumers, and open new revenue streams.
These developments align closely with the themes covered on upbizinfo.com/business.html and upbizinfo.com/markets.html, where new business models-such as energy-as-a-service, virtual power plants, and performance-based contracts-are reshaping how energy is sold, financed, and managed. For marketers and strategists following upbizinfo.com/marketing.html, the implication is that energy is increasingly a differentiated service experience, not just a commodity, and customer engagement around sustainability, transparency, and digital convenience is becoming a competitive battleground.
Corporate Strategy, Brand Trust, and Net-Zero Commitments
By 2026, net-zero commitments have become a litmus test of corporate seriousness about the future. Leading companies across sectors-from technology and finance to manufacturing, retail, and logistics-are setting science-based targets and integrating decarbonization into governance, capital budgeting, and product strategy. Organizations such as Microsoft, Apple, Google, Amazon, Volkswagen, Hyundai, IKEA, and Unilever are leveraging renewables not only to cut emissions but also to strengthen brand equity and attract talent and investors who prioritize environmental performance.
Coalitions like RE100, the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), and disclosure platforms such as CDP (Carbon Disclosure Project) have created standardized frameworks for measuring and communicating progress, which in turn are used by institutional investors, rating agencies, and regulators to assess credibility. The result is a feedback loop in which robust climate action enhances access to capital and market share, while weak or misleading claims risk regulatory scrutiny and reputational damage.
For the audience of upbizinfo.com, this is not merely a sustainability narrative but a core business and risk management issue. Boards and executives are increasingly aware that credible renewable strategies are essential to maintaining trust with stakeholders across United States, United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Nordic countries, Canada, Australia, Japan, Singapore, and fast-growing markets in Asia, Africa, and South America. Articles on upbizinfo.com/news.html and upbizinfo.com/sustainable.html reflect how this trust dimension is influencing deal-making, partnerships, and competitive positioning.
Equity, Inclusion, and the Social Dimension of Transition
A credible energy transition must also be a fair one. More than 700 million people worldwide still lack access to electricity, and many more suffer from unreliable or unaffordable power. At the same time, communities dependent on fossil fuel industries face economic disruption as demand patterns shift. The concept of a "just transition" has therefore become central to policy debates, with emphasis on ensuring that climate action does not exacerbate inequality within or between countries.
Programs supported by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), the International Labour Organization (ILO), and regional development banks aim to align renewable deployment with social objectives such as job creation, gender equity, and rural development. In Africa, initiatives like the Africa Renewable Energy Initiative (AREI) and the Africa Clean Energy Corridor are working to expand access through a combination of grid extensions, mini-grids, and solar home systems, often using mobile-based payment models that enable low-income households to pay for energy incrementally. Similar patterns are visible in South Asia, where companies like M-KOPA and d.light have demonstrated how off-grid solar can support entrepreneurship and improve living standards.
For business leaders, investors, and entrepreneurs following upbizinfo.com/founders.html and upbizinfo.com/world.html, these efforts highlight a critical opportunity: aligning profitability with inclusive growth by designing products, services, and financing models that expand access while maintaining commercial viability.
Looking Ahead: Strategic Implications for Business and Markets
As the world moves deeper into the 2020s, the renewable transition is no longer a peripheral trend; it is a defining context for strategic decision-making across all the sectors and regions that upbizinfo.com serves. For businesses in North America, Europe, Asia, Africa, and South America, the key imperatives include securing reliable access to clean energy, managing exposure to carbon and transition risks, positioning in growth segments such as storage and hydrogen, and building the skills and partnerships needed to thrive in a low-carbon economy.
For financial institutions, the transition is reshaping credit risk, asset valuation, and product innovation, making climate and energy literacy as essential as traditional financial analysis. For workers and job seekers, it is redefining career paths and skills requirements across engineering, data science, operations, marketing, and management. For policymakers, it demands an ongoing balancing act between ambition, affordability, security, and social cohesion.
In this environment, the mission of upbizinfo.com-to provide clear, authoritative, and actionable insight across business, technology, markets, economy, and sustainability-becomes even more critical. By connecting developments in AI, banking, crypto, employment, investment, and global policy to the overarching narrative of the energy transition, the platform equips decision-makers to navigate uncertainty with confidence and foresight.
The trajectory toward a predominantly renewable energy system is now firmly established, but its ultimate shape and pace will depend on choices made in boardrooms, parliaments, laboratories, and communities over the next decade. Organizations that treat this transition as a core strategic lens-not a compliance exercise-will be best positioned to capture new value, manage risk, and build enduring trust in a world where clean energy is not just a technology, but a foundation of economic and social resilience. For readers seeking to stay ahead of these shifts, upbizinfo.com will remain a dedicated partner in interpreting the signals, connecting the dots, and highlighting the opportunities emerging from this historic transformation.